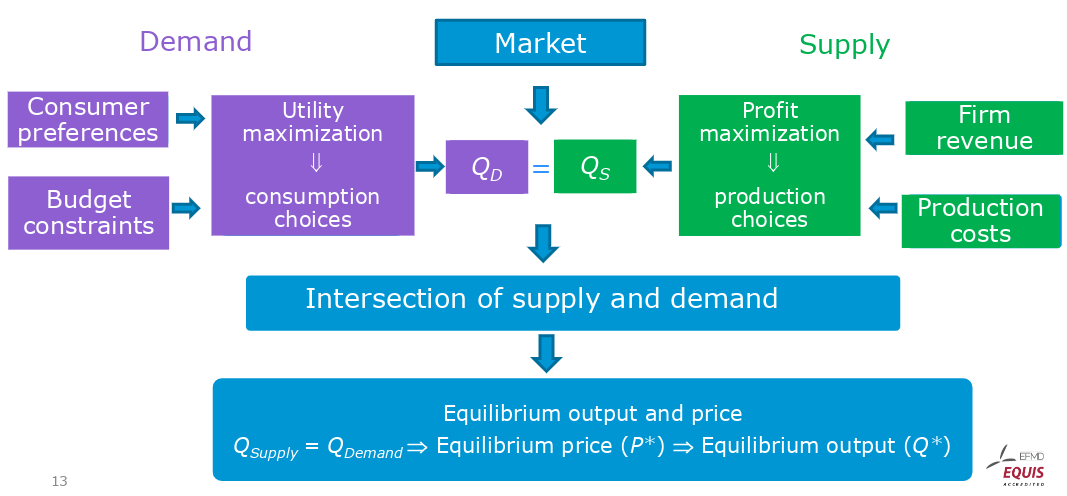
-
each consumer makes individual choices
-
aggregation of all consumers creates the demand
-
consumer faces value maximization problem
-
each company makes individual choices
-
aggregation of all companies creates the supply
-
company faces profit maximization problem
Supply and Demand require Competition! There cannot be Supply and Demand in a Monopoly.
Supply
- variable
- price of the good
- constants (can change over time)
- technology → Feral Futures, Disruptive Technologies
- prices of inputs
- taxes
Demand
- variable
- price of the good
- constants (can change over time)
- preferences → Customer Perspective
- income → Poverty, Prahalad
- prices of other goods
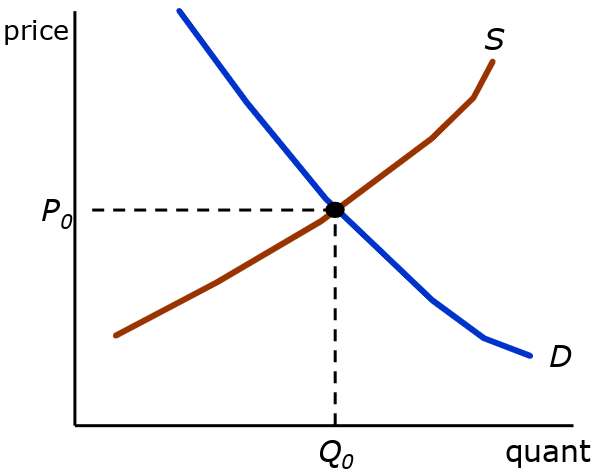
Equilibrium
- intersection of supply and demand function
- Game Theory → no need to act by either consumer or producer
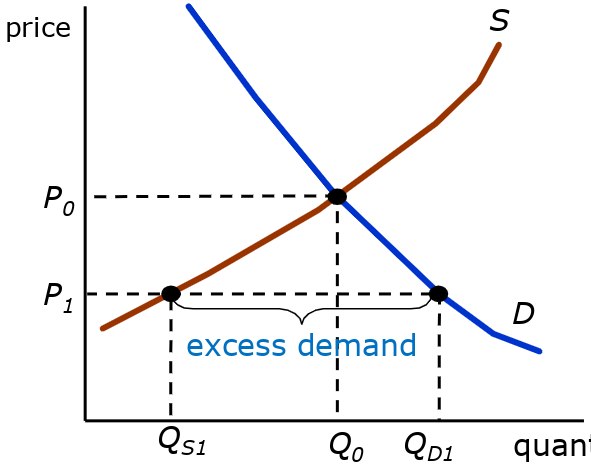
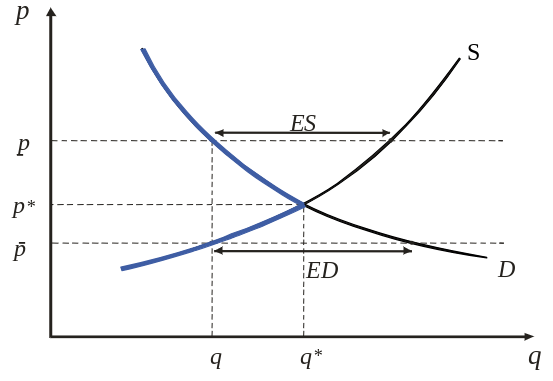
Excess Demand
- consumers demand more than suppliers are willing to supply
- price will increase, supply will increase, demand will decrease
- reaching equilibrium eventually → convergence
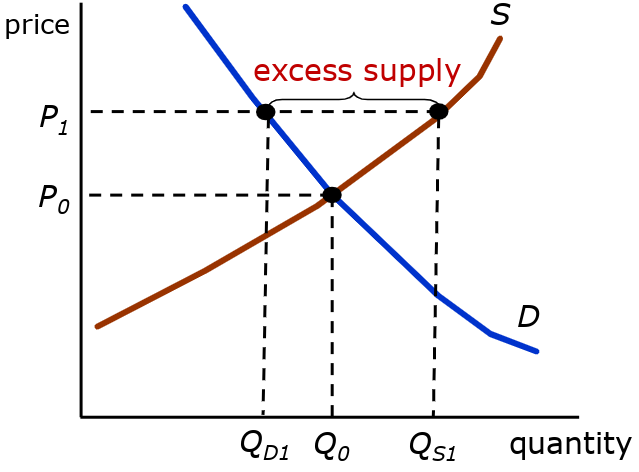
Excess Supply
- consumers demand less than suppliers are willing to supply
- price will decrease, supply will decrease, demand will increase
- reaching equilibrium eventually → convergence
Market Mechanism
- there is only too little supply or too little demand
Shift Equilibrium
- change of supply inversely affects price
- change of demand directly affects price
Price Elasticity
- Marginal Changes
- Elasticity
- Cross-Elasticity
- price elasticity of demand ⇐ 0
- price elasticity of supply >= 0
- “arc elasticity” … taking the average slope along a price range
- used for analyzing the sensitivity of different variables