What is Finance?
- I need money. Where can I get it from?
- grandma
- bank loan
- financial markets
- I have money. Where can I put it in?
- bank
- invest in property, art, etc
- financial markets
Scope
- financial markets
- instruments traded on financial markets
- how are prices formed
- performance/risk
- notions on profitability/risk
- expected returns, “beating the market”, when does risk matter?
Dimensions of Data
- cross-sectional data
- different entities at the same time
- horizontal vector
- time-series data
- same entity at different times
- vertical vector
- panel data
- different entities at different times
- matrix / dataframe
Sources of Financial Data
- market data
- trade related, transactions on a financial market
- e.g. prices, trading volumes
- accounting data
- survey data
- e.g. LIBOR, market sentiment indices, etc
- data providers (academic and industry providers)
Financial Markets and Instruments
- instrument … something listed on a financial market
- exchange traded
- stocks
- futures, ETFs, some options, etc
- price set by supply/demand
- more regulated environment (trading hours, disclosure requirements, etc)
- over the counter (OTC)
- bonds
- forwards, funds, options, etc
- price set by seller, buyer accepts/declines
- few regulations
Stocks
- you become an owner of the firm if you hold its stocks
- equity is divided into pieces called stocks/shares
- proportional to the number of shares
- usually entails voting rights
- Dividend payed out to shareholders
- vary over time, depending on profit of firm
- Limited Liability - cannot lose more than the shares you own
- in case of default - read here
Bonds
- you become a creditor of the frim if you hold its bonds
- debt financing
- more participants than just a single entity (e.g. bank)
- a “big loan” is divided into smaller ones - bonds
- transfer of bond is easier than shares
- coupons … regular interest payment, usually annual or semi-annual
- like interest, just payed to you
- repayment … the fixed date when the bond is payed back
- called maturity (5y, 10y, 15y)
- e.g. buying a bond with 5y maturity for 10k, after 5y you will receive the 5k back from the company
- primary vs secondary markets
- primary: sold for the first time, IPO, company sets its own beginning prices
- secondary: bought and sold between investors, e.g. on the NYSE
- price discovery: supply/demand
- primary: book building
- secondary: order book
Book building - Simplified
- used for OTC sales
- set reasonable price for stock
- road show … advertise the security to investors or general public
- customers send offers … x amount for y each
- add up the demand and offers
- choose price according to those offers
- allocate stocks to the buyers
- maximize number of transactions
- if there are more offers than supply
- choose highest price to sell all your supply
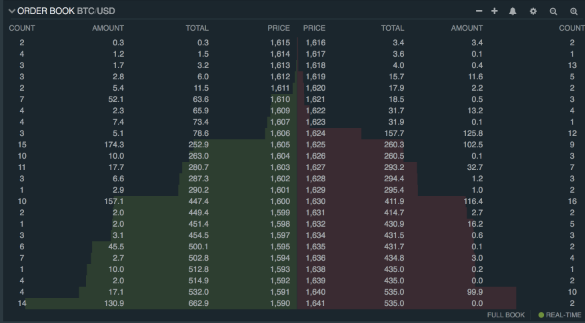
Order Book - Simplified
- used on exchanges
- bid price … what you want to sell it for
- ask price … how much you are willing to pay
- if there is a match i.e. bid price < ask price the transaction is executed
Prices to Returns
- one cannot compare prices, only performance
- performance … relative price change over time interval
- simple return: rt=pt−1pt−pt−1=pt−1pt−1
- log return: rtl=log(pt/pt−1)
- note: rt=ertl−1
Stylized Facts
- returns are hard to predict
- maybe 1 minute into the future
- returns have fat-tailed distributions
- more extreme observations than in normal distributions
- normally smoother curve, peak not as high
- average is normally around 0
- volatility clusters
- volatility … different between high/low
- volatility is “exploding” during short times and stays like that for a short while before calming down again
- correlation tends to spike/increase during market downturns / crashes
- individual stocks follow downwards but move up separately
