Maths of Correlation
-
covariance
- Covariance
- Covariance and Correlation
- reminder: independent (unrelated) → covariance = 0
- BUT covariance = 0 does not imply independence
- estimation
-
correlation coefficient (Karl Pearson)
- for population:
- for sample:
-
notation
- … sum of squared standard deviations
- is to be minimized in method of least squares
-
equivalent representation
-
correlation is measure of linear relation
-
correlation does not mean causality
-
… between -1 and 1
- sign indicates direction of the correlation
-
shows the strength of the correlation
-
… symmetrical
Proof of
- given
- short form:
- long from: Proof of Correlation Coefficient
- is -1 or 1, depending on sign of
Non-Linear Correlation
- if the data has non-linear correlation (e.g. quadratic, exponential) it is impossible to measure with
- but might be possible with e.g
- a scatter plot is always helpful to understand the problem and choose the correct correlation function
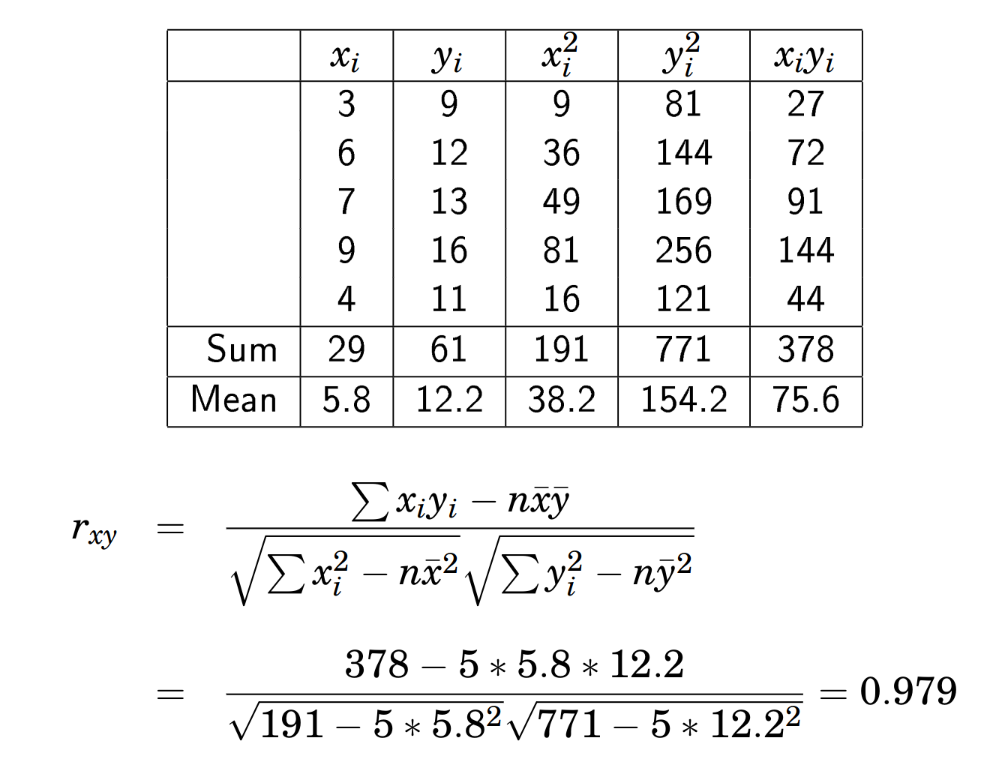
Example Correlation from Table