Glossary
Info
subscript and superscript used mixed on the slides e.g. can be found instead of , but it is identical
- and … Supply and Demand
- supply = all of all firms added up
- and … Revenue and Costs
- … fixed costs
- … Quantity of x
- … Price of x
- … Elasticity of x
- … Optimum/Equilibrium of X (Price, Quantity)
- sometimes used as and in duopoly
- … another Optimum of X
- e.g. when comparing competition vs monopoly
- … Profit of x
- … joint profits
- … Marginal X (Revenue/Costs/Profit)
- … Average X (Costs, Variable Costs, Revenue)
- … total X (costs, revenues)
Basics
Important
I use capital letters in general formulas or for results, lowercase letters for inputs and when using the formulas. When calculating the equilibrium quantity I use When calculating the profit at a quantity I use
- Equilibrium:
- Elasticity:
- Cross-Elasticity:
Perfect Competition
- Maximization:
- at :
- Profit:
- Supply:
- fixed costs included
- long run: … more competitors enter market, price falls until and
Monopoly
- … Revenue function with twice the slope → why?
- optimal price rule of thumb:
- … … markup
Third Degree Price Discrimination
Two-Part Tariffs
- … per-unit price; … buy-in price (lump-sum fee)
- or
- … consumer surplus of the consumer group with smaller demand
- (linear demand curve → triangle)
-
- if
- … amount of customers in all groups, … amount of consumer groups
Oligopoly
Collusion / Cartels
- just use the Monopoly instead of oligopoly formulas
When what?
Competition on (x + y) results in behavior:
- price + sequential = price leadership
- quantity + sequential = quantity leadership (Stackelberg)
- price + simultaneous = Bertrand
- quantity + simultaneous = Cournot
Price Leadership
- firm 1 sets price in anticipation of firm 2’s reaction
- firm 2 takes price of firm 1 as given, adjusts accordingly
-
- … parameters
Stackelberg
- firm 1 sets output in anticipation of firm 2’s reaction
- firm 2 takes output of firm 1 as given, adjusts accordingly
-
- … parameters
Bertrand
- maximized price (same for ):
Cournot
- optimized quantity (same for ):
Amoroso-Robinson Formula
-
- … elasticity of demand (not market elasticity)
- perfect competition:
- loss of demand with small price change
- market power/monopoly:
- negatively sloped market demand & marginal revenue curves
- inelastic demand:
- negative marginal revenue → not optimal!
Lerner Index
→ perfect competition → monopoly
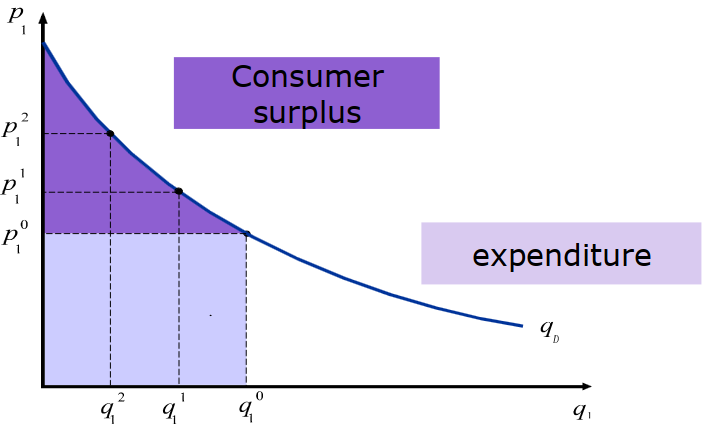
Surplus
Consumer Surplus
- area between demand function and given price
- derivative - rectangle
- OR with linear quantity just a rectangle ()
Tax Burden
- on consumers:
- on sellers: