- Constitution
- new fundamental rights can also create new basic values
- Separation of Powers
- Hierarchy of Norms
- Basic Principles
- Constitution
- Ordinary Laws
- Ordinances → Ruligns by Administration → Verordnung
- Rulings, Judgements, Decisions → individual cases
- Federal Legislation
- Diet … Parliament of Land
Credit: Aaron Meekins
Constitution and Functions
- Constitution
- Basic document of State legal order
- Highest rank in legal order
- Higher hurdles for modification
- Higher rank in the legal order compared to other legal documents
- Basic document of State legal order
- Functions
- Rules for political process
- Enactment of laws
- Actions done by high politicians in government
- Rule, regulate, set the games of political process
- No politician may step outside of this
- Separation of Powers
- Fundamental Rights
- Basic values
- Common goals
- Rules for political process
Introduction
- Federal Constitutional Act of 1920 (Bundes Verfassungsgesetz)
- Basic principles of the constitution
- Organization structure
- Powers of institutions and bodies
- Fundamental rights
- Federal constitutional law spread among various legal instruments
- Austria is a federal state. There are nine Land Constitutions
- Other constitutional acts and constitutional provisions in various legal acts
- Specific act on security
- Specific act on neutrality
- Not every provision is in the constitutional act of 1920
- Hierarchy of Norms
Basic Principles of Constitution
- Not listed in the constitution
- Customs
- Characteristics
- Democratic Principle
- Republican Principle
- Federal Principle
- Rule of Law (Rechtsstaat)
- Liberal Principle
- Separation of Powers
- Unconstitutional constitutional law
- Ordinary constitutional law in conflict with one of the basic principles
- Special rules of enactment and amendment
- Only one referendum in Austrian history
- When Austria joined the EU (1994)
- Two different versions of constitutional law
- Article 44
- We can make a distinction between a complete amendment of the constitution and a partial amendment of the constitution
- For a complete, there’s procedures that have to be followed
- Stricter than a partial change
- For a partial amendment, there’s separate procedures
- For a complete, there’s procedures that have to be followed
- If a basic principle is amended or deleted, article 44 says this is a complete revision of the constitution and the parliament has to approve by ⅔ while 50% of parliamentarians are present.
- Referendum
- Only one referendum in Austrian history
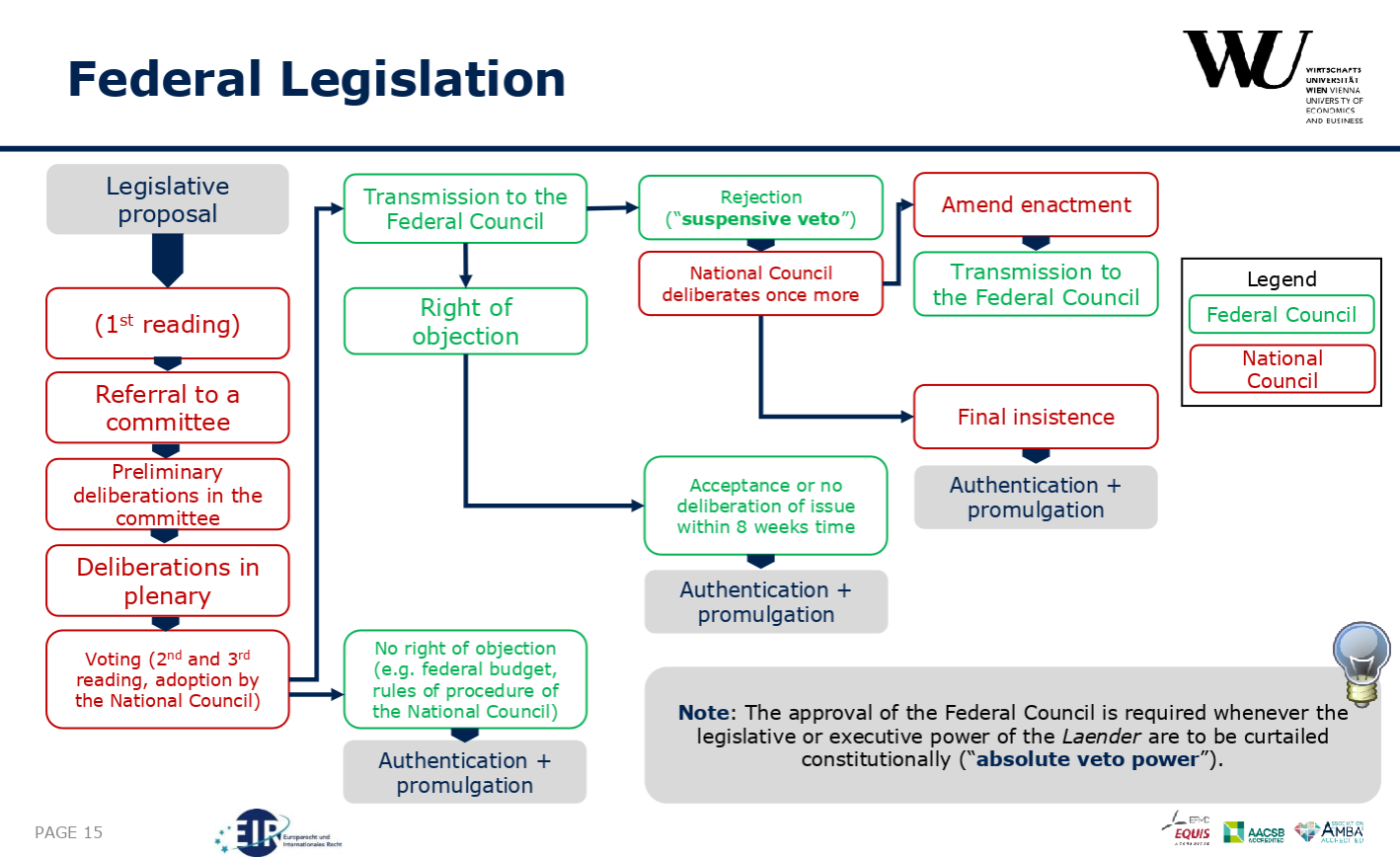
Federal Legislation
Federal Legislation
- red: National Council → Nationalrat
- green: Federal Council → Bundesrat
- suspensive veto
- like a stop! button for the law
- is overruled by another transmission
Authentication … approval of Federal President promulgation … official publication
Credit: Aaron Meekins
Link to original
- Legislation process on a federal level
- Who can give the initiative for a law?
- Parliament
- Federal Council
- Popular initiative
- Government (all of the ministers)
- Legislative proposal happens
- First reading
- Referral to a committee
- Preliminary deliberations in committee
- Deliberations in plenary
- Voting
- 2nd and 3rd reading, adoption by the National Council
- No right of objection
- Federal budget
- Rules of procedure of the national council
- Transmission to the Federal council
- Right to a suspensive veto
- National council deliberates once more
- Final insistence
- Authentication + Promulgation
- Right of objection
- 8 weeks to deliberate
- Right to pause
Executive
- Highest Executive Bodies
- Federal President
- Federal Government
- Collegiate body (Many members)
- Chancellor
- Same “position” as the ministers
- Vice Chancellor
- Ministers
- Chancellor
- Collegiate body (Many members)
- Federal Ministers
- Every minister has parts directly under their control
- Minister of health
- Parts of other ministers jurisdiction also come under the minister of health
- Minister of health
- Every minister has parts directly under their control
- Executive Power of Federation
- Direct federal administration
- Federal authorities
- Police
- Financial administration
- Federal authorities
- Indirect federal administration
- Governor (Landeshauptmann)
- Subordinated Land authorities
- Where Laender have power in the constitutional system
- Direct federal administration
Federal Government
- Appointed by the Federal President
- Dismissal by the Federal President…
- Of the the chancellor/the entire Federal Government: no recommendation required
- Of individual members: recommendation of the Federal Chancellor
- Removal from office by way of vote of no confidence (National Council) or resignation
- Federal Government (collegiate body) ←Distinguish→ Federal Minister
Judiciary
- Ordinary Courts/ Criminal Courts
- Supreme Court of Justice
- Higher Regional Courts
- Regional Courts
- District Courts
- Courts of Public Law
- Administrative Jurisdiction
- Examine whether administrative acts comply with the law
- Constitutional Court (Guardian of the constitution)
- Powers to review laws and regulations for their constitutionality
- Court of fundamental rights
- Resolves conflicts of competence between the federation and a Land or between the Laender themselves
- Pronounces upon challenges to elections
- Supreme Administrative Court
- Court of final instance in administrative matters
- 11 Courts of First Instance
- 9 Land Administrative Courts
- Federal Administrative Courts
- Federal Finance Court
- 11 Courts of First Instance
- Court of final instance in administrative matters
- Administrative Jurisdiction