Principle
- working capital = current assets - current liabilities
- working capital → money which is not resulting in long-term profits
- current assets are used to build and sustain revenue
- long term profits come from non-current assets
- e.g. new machines → cheaper production → larger margin
Too High Working Capital
- might be too much Inventory → hard to sell
- many firms are trying to reduce their working capital
Working Capital Cycle
Transclude of Production_Cycle.excalidraw
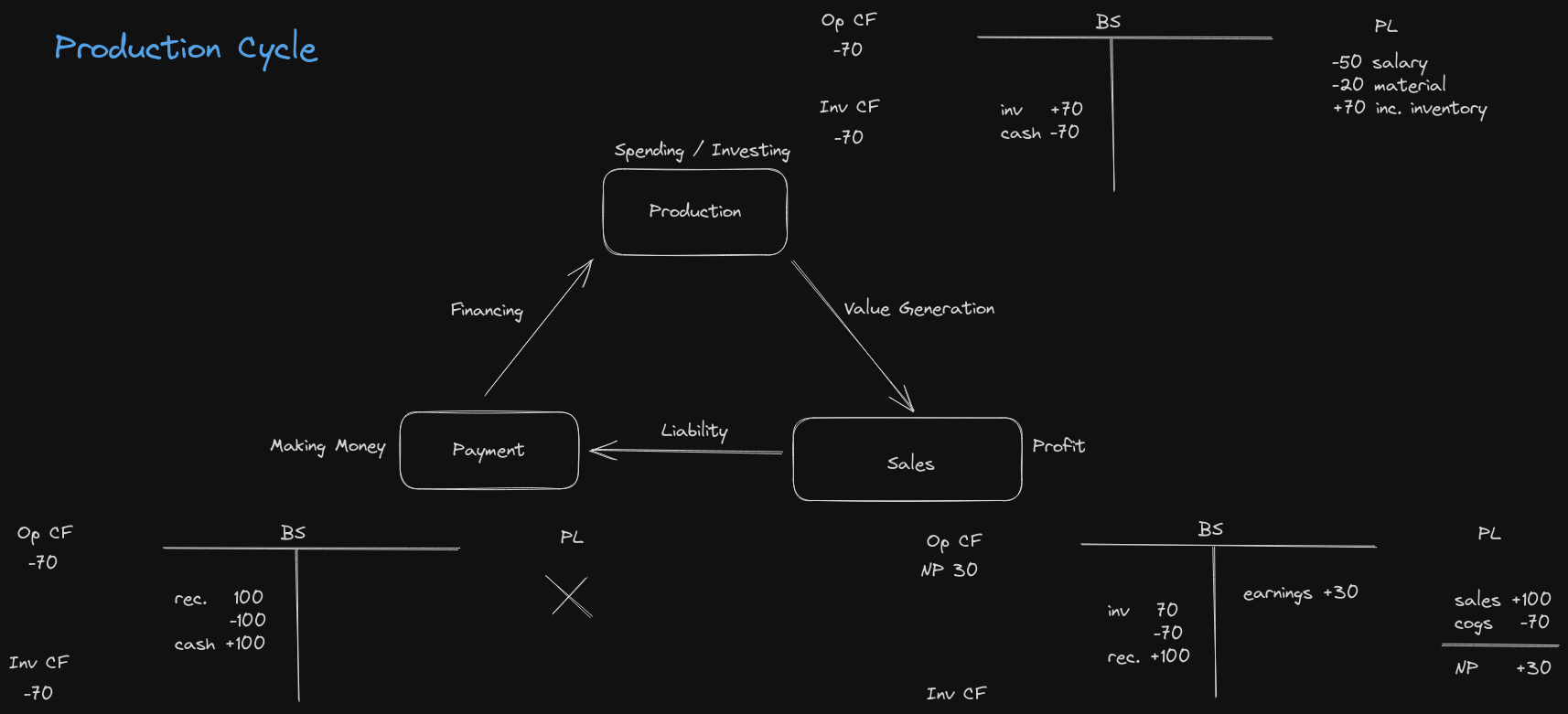
Balance Sheet and P/L
- Buy Resources (+20 inventory, +20 liabilities)
- work-in-progress and finished goods
- Produce Products (+15 inventory, -15 cash)
- Sales → Receivables (+50 receivables, -35 inventory, +15 retained earnings)
- P/L (Sales +50, Cost of Goods Sold -35 = 15 Profit)
- Receivables → Cash Flow (+50 cash, -50 receivables) (P/L 0)
- Cash Flow → paying Payables (-20 cash, -20 liabilities)
- Produce or Buy Inventory → circle continues
Same with Cash Flow
- start with EBT: +15
-
- increase in inventory: -20
-
- increase in liabilities: +20
-
- spending in production: -15 ← actual cash flow
-
- reduction in inventory: +35
-
- increase in receivables: -50
- until here sum is 0 → no cash has flown yet
-
- decrease in receivables: +50 ← actual cash flow
-
- decrease in liability: -20 ← actual cash flow
- = +15 → positive cash flow
