Why is it important?
- climate scientist underestimate recent warming effects
- extreme weather anomalies reaching higher than ever before
- Austria
- average temperature deviation rising
- +2.6 degrees on average, more in cities than in mountains
ESRS
GHG Protocol Standards
- product carbon footprint
- technically hard to calculate
- 2 different perspectives on the same emissions
- e.g. apple, emissions of the whole company vs emissions per iPhone produced
- not double-counting, since it is the same emissions, but different perspective
- one could also argue everything is double counted…
Generally Accepted GHG Accounting Principles
- relevance
- report must reflect the actual emissions
- completeness
- consistency
- consistency over time to allow for easy comparison
- transparency
- data sources
- assumptions
- calculations
- accuracy
- everything is an estimation
- but the goal is to remove uncertainties and not over/underrepresent emissions
GHG Accounting Process Steps
- get data
- decide on boundaries and calculation schemes
- also dependent on data available
- boundaries for organization and for operations
- analyse data and calculate GHG Emissions
- stick to it and report correctly
Setting Organizational Boundaries
- equity share approach
- control approach
- if there is operational control the emissions of the controlled entity are 100% of the controlling entity
Scope 1 Emissions
- identify sources
- stationary/mobile combustion, fugitive emissions, process emissions
- select calculation approach
- direct measurement, stoichiometric calculations, estimates
- collect data and choose emissions factors
- mostly emission data is written on the invoice
- just not integrated yet in the ERP system of most companies
- would allow for integrated calculations
- data levels
- primary: consumption in liters of fuel
- secondary: mileage of car
- tertiary: amount spent on fuel
- apply calculation tool
- convert all emissions to CO2eq
- roll-up data to corporate level
Scope 2 Emissions
- identify sources
- electricity, steam, heat, cooling
- select calculation approach
- market based vs location based approach
- location … geographic location
- market … contracts, purposeful decision
- collect data and choose emissions factors
- metered electricity, utility bills
- consumption in kWh
- emissions per kWh from different energy providers
- apply calculation tools
- convert all emissions into CO2eq
- roll-up data to corporate level
Scope 3 Emissions
- GHG Protocol
- screening
- based on all 15 categories of GHG Protocol
- identify significant categories based on estimated emissions
- calculation
- calculate and estimate as best as possible
- update
- update scope 3 every year
- full inventory (scope 1 and 2 too) only every 3 years
- or when significant change
- not include
- emission offsetting / emission trading → transparency
- reflect actual emissions
Process
- describe the value chain
- data collection and initial assessment
- supplier data
- hybrid data
- average data (secondary process data)
- e.g. aggregate miles of flights booked
- spend-based data (tertiary accounting data)
- e.g. aggregate of cost of flights booked
- materaility and screening → Materiality Assesment
- selection of relevant categories
- selection of calculation methods and calculation
- depends on data available
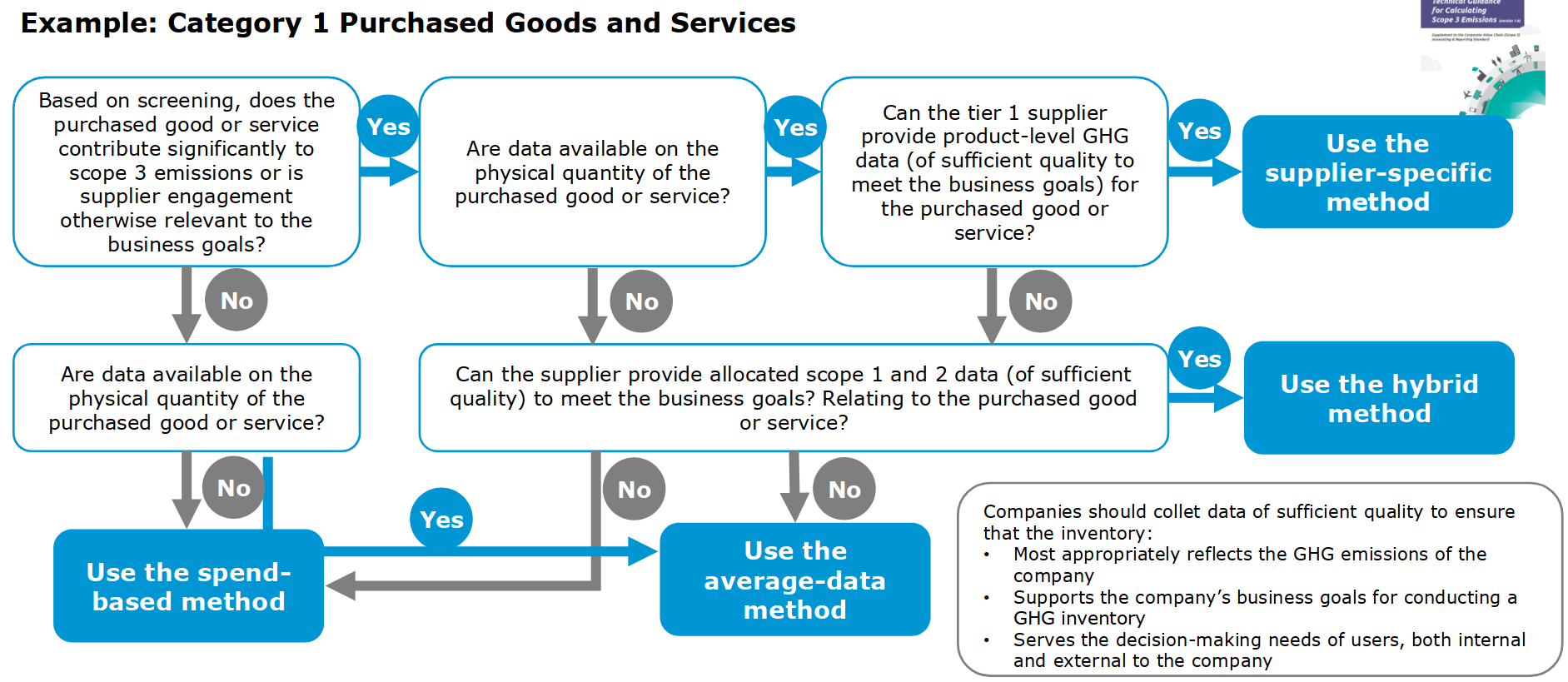
- supplier-specific method
- aggregate of all suppliers
- hybrid method
- aggregate of supplier data you have, extrapolate for the rest
- average data method
- take average of emissions per unit consumed you have, multiply by consumption
- spend-base method
- take average of emissions per expenses you have, multiply by expenses
- results and interpretation
Neutrality vs Net Zero
Climate Transition Plan
- compatibility with paris agreement
- decarbonization levers
- quantification of investments
- climate change mitigation actions
- locked-in GHG Emissions
- e.g. a new plant has been built 5 years ago which is running on gas-generators
- that plant will not be touched in the next 20 years probably
- taxonomy regulation
- plans on reaching higher alignment
- business strategy
SBTi
