Globalization, Specialization, Free Markets
- integrated commodity markets
- greater world trade, broader range of goods
- Division of Labor
- industrial vs peripheral economies
Globalization - What?
- History
- fast growth between 1840 and 1900 - idea of progress
- 1918 - 1950 doubt about progress idea
- globalization
- globalization measured in Market Integration
- Movement of X goods, labor, capital, land more/easier
- movement of land … conquest of settlement, Imperialism, migration
- political, social, cultural, regulatory, etc implications
Specialization - What?
Glob and Spec - Why?
- industrial revolution spread from UK → Industrial Revolution … Again
- industrialization slow in the rest of the world
- value of 16 … industrialization level of UK in 1800
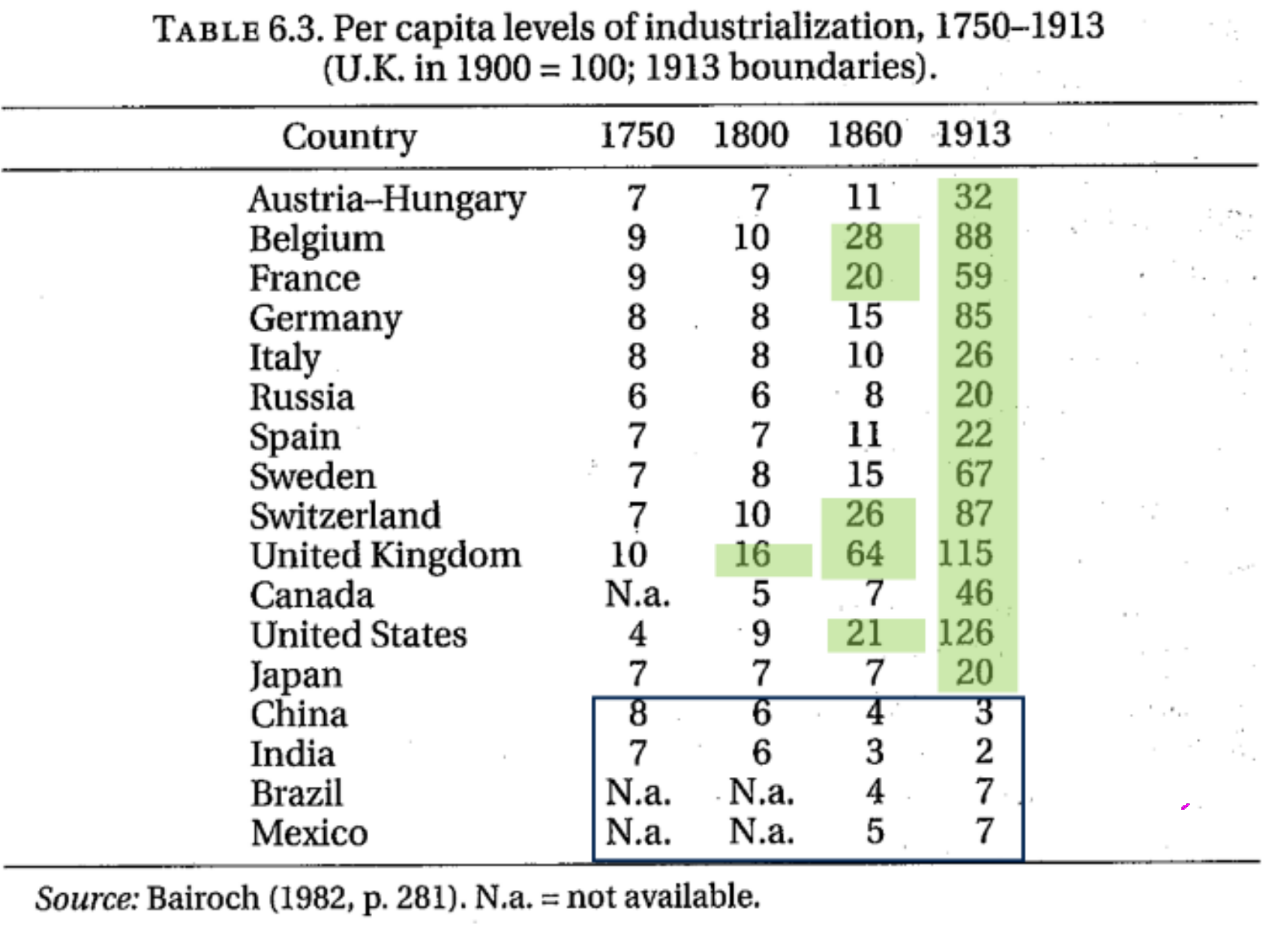
- value of 16 … industrialization level of UK in 1800
Role of Trade
- raw materials and food for core countries
- e.g. raw cotton to UK
- consume produced products
- e.g. cotton cloth from UK
- → Market Integration
- can overproduce locally and sell to other countries
- actively search for new markets
- slightly higher export prices over time
Trade and Transaction Costs
Trade Policy Liberalization
- lowered import/export tariffs (first in UK, then the rest)
- AVE … tariffs
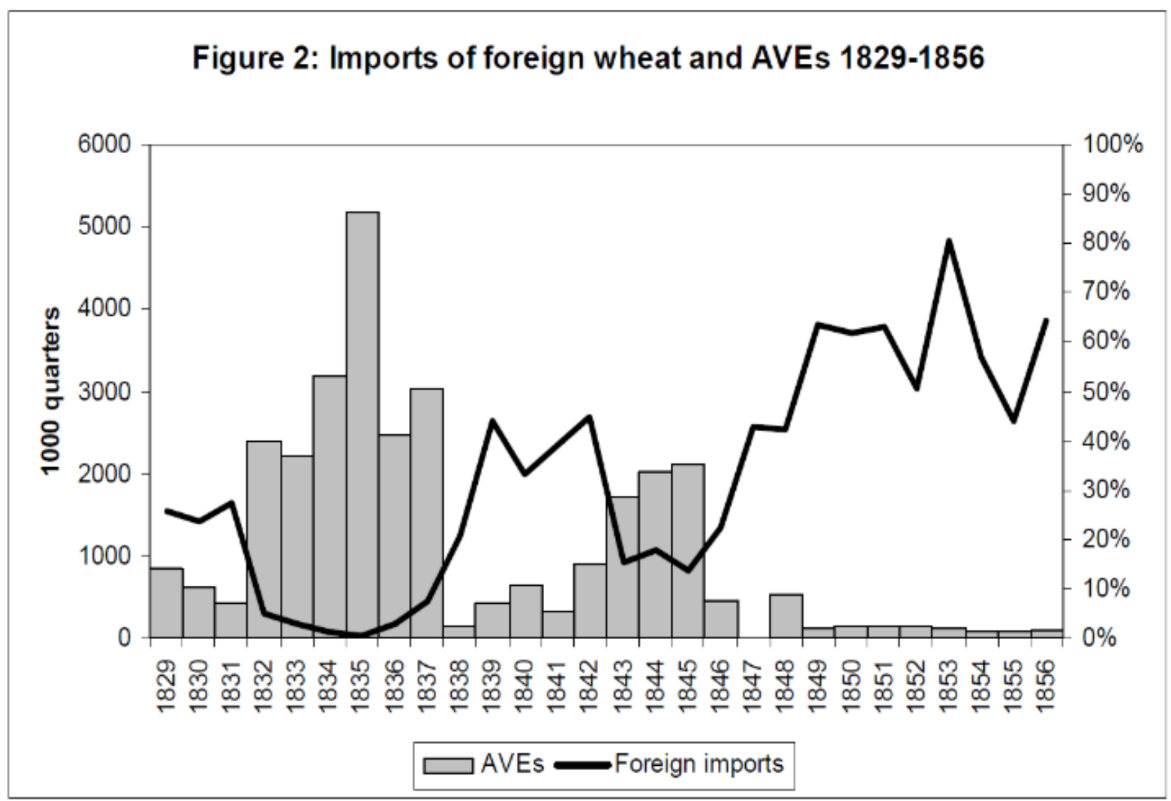
example: japan opening after 1853
- Harris treaty of 1858
- Comparative Advantage emerged naturally
- Silk, silkworm eggs, tea exported
- cotton yarn, sugar, rice imported
- industrialization happening after opening
Gold Standard
Peace in Europe
- before 1815 europe in war all the time
- embargoes → cant trade with enemy
- privateering → private pirates instead of actual navies
- wartime → merchant ships converted into warships
- uncertainty
Imperialism
International Migration
- suitable cultivation areas used productively
- larger share of transnational vs national migration and greater total migration
- mostly from Britain (40%) to US (60%)
International Investment
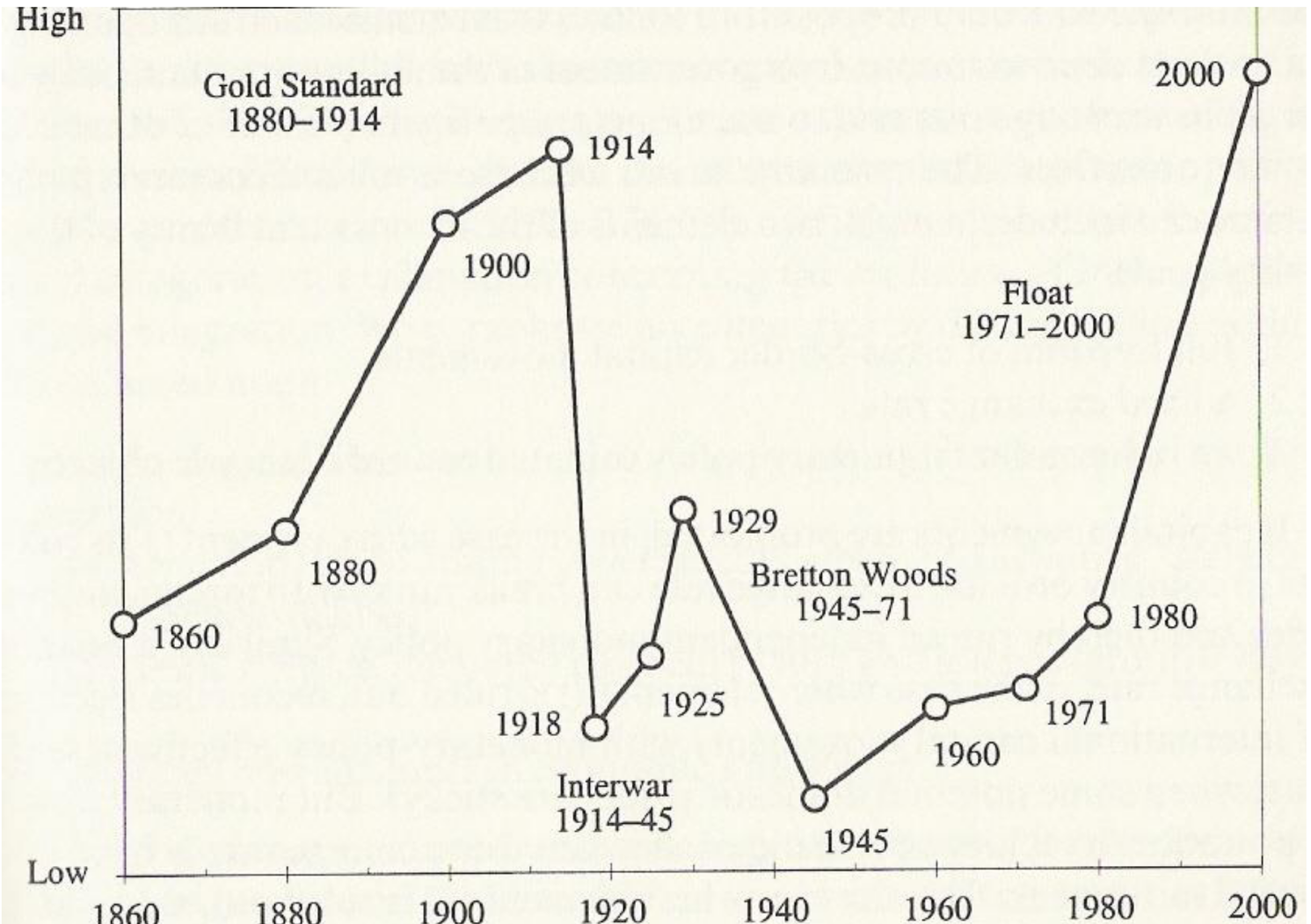
-
90% of those investments from industrializing European areas which need raw materials
- exporting population for imports of raw materials
- North America, Europe, Latin America (Argentina Brazil), Ozeania
- 43% from Britain, 20% Franc, 13% Germany
- invenstments went where the migration went
- mostly Europe, US, Latin America; a bit of Asia too
- institutions similar to investment source
- Why invest abroad?
- higher returns on capital for increased uncertainty/risk
- migrating population younger than average, no/little savings
- if savings, spent on travel and setup
- high fertility rate, low savings in migrated locations → Script 2 Summary
- high need for infrastructure → high interest rates
- abundant land, secure institutions and good productivity → benefits of investments high too
Glob and Spec - Consequences
Prices converging
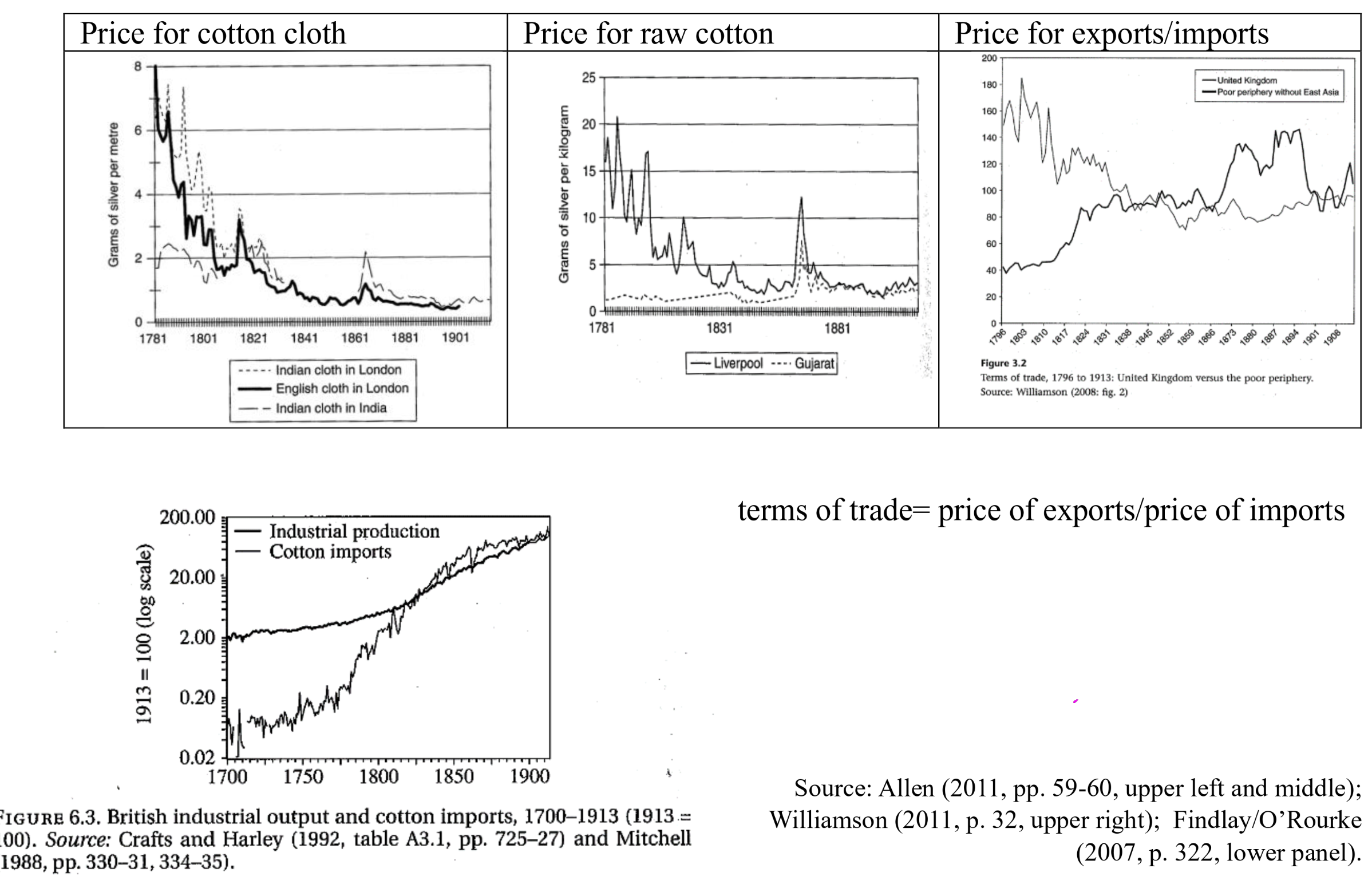
Consequences
- spread of industrialization
- source of growth
- core countries had 80% of the market
- core countries determined development of the rest of the world
- periphery countries were dependent on core countries and their relation to them