Governance Structure
Legislation
NFRD or NaDiVeG
- responsibility for reporting and supervision
- supervisory board needs to check if the published report looks okay
- after supervisory board approves it is included in annual report
CSRD
- new reporting requirement
- expertise and skills, roles, incentive schemes of management and supervisory board need to be disclosed
- responsibility for supervision
- tasks of the audit committee (i.e. subset of supervisory board to check on the sustainability report)
Management Level
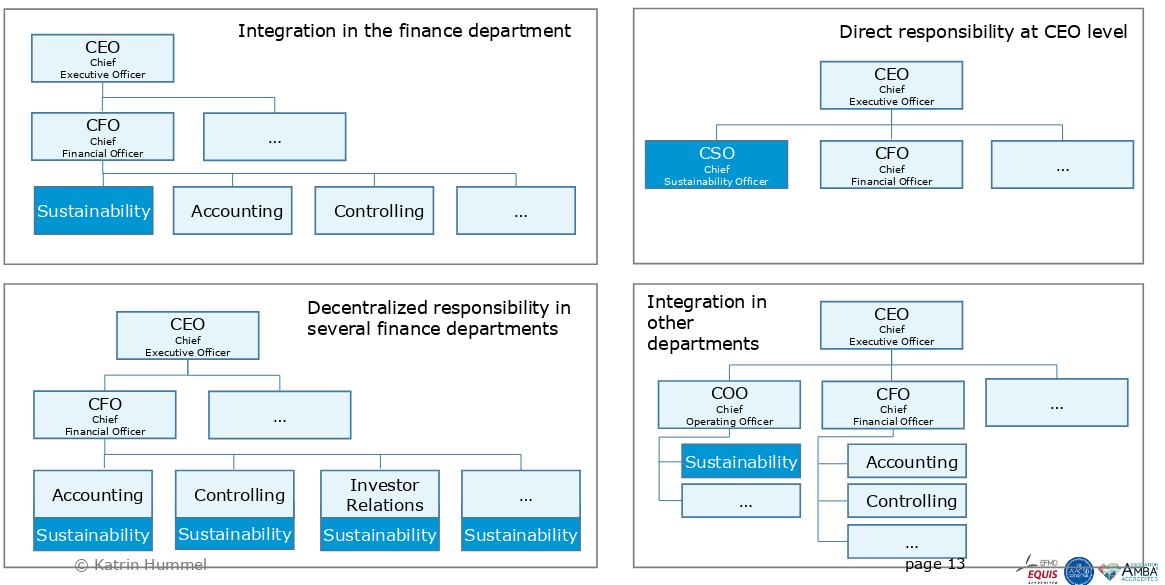
Types
- financial-centered sustainability department reporting to CFO
- operation-centered sustainability department reporting to COO
- chief sustainability officer CSO operating across departments
- best results in terms of international studies
- done by The Big 4
- best results in terms of international studies
- different sub-departments or people regarding sustainability in each department
Supervisory Level
- checking content of the sustainabiltiy report
- 3-20 members dependent on size of company
- works typically in committees (renumeration, nomiation, audit, …)
Types
- just audit committee (smaller companies)
- audit committee + sustainability expert
- extra sustainability committee (large enterprises)
Organizational Embeddedness
- general sustainability reporting lies with CEO
- finance department may do the data analysis and the “sustainability accounting”, but actually implementing and improving their sustainability lies with other people
Empirical Evidence
- wontfix sr 6 18
Incentive Schemes
- applicable renumeration for management level
- creates incentive for board members to care about sustainability
Empirical Evidence
wontfix sr 6 20
# Sustainability Strategy
Ambition Levels
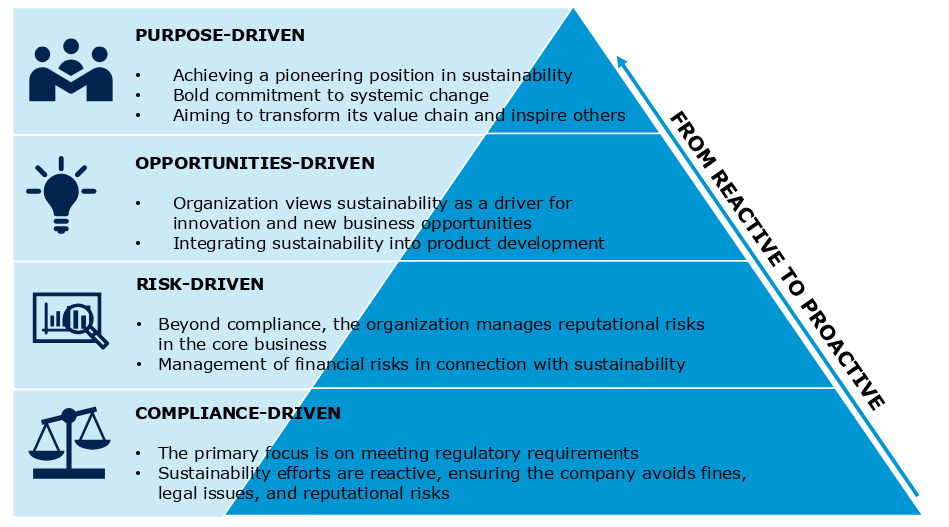
- purpose-driven:
- going above and beyond
- (hopefully) positive stakeholder reaction
- opportunities-driven:
- use EU Taxonomy Regulation for innovation ideas, not just for mandatory reporting
- risk-driven:
- risk of public/shareholder pressure
- risk of effects of climate change and environmental damage
- compliance-driven:
- rather comply than face sanctions
Strategy
Stakeholder Engagement
- determine material sustainability matters
- develop, vision, mission, strategy
- attitude about climate protection
- define goals and targets
- intermediate targets to reach final goals:
- GHG Emissions scope 1 and 2 net-zero by 2040
- GHG Emissions net-zero including scope 3
Employee Engagement
- define KPIs
- energy efficiency in operations
- percentage of renewable energy
- percentage of EVs in fleet
- define actions
- examples:
- joining SBTi
- reduction of leakage in operations
- purchase of renewable energy
- installment of PVs
- purchase of EVs
- examples:
- monitoring
- establish internal systems to regularly monitor progress and achievements
- adjust the strategy as needed to respond to changing conditions
Define Targets
- key characteristics
- SMART targets
- public commitment
- transparency, reputation
- inputs for target setting
- benchmarking with competitors
- regulatory targets
- stakeholder expectations
- process of target setting
- how to change current performance
Define Actions
- employee engagement
- awareness, awards, prizes
- culture of sustainability → corporate culture
- technology and innovation
- new technologies, artificial intelligence maybe?
- cross-functional collaboration
- alignment across departments
- integrated solutions
- evaluation of actions
- criteria for effective measures
- confidence level, strategic relevance, time-horizon, reputation (greenwashing), etc
Data Management and KPIs
The Issue
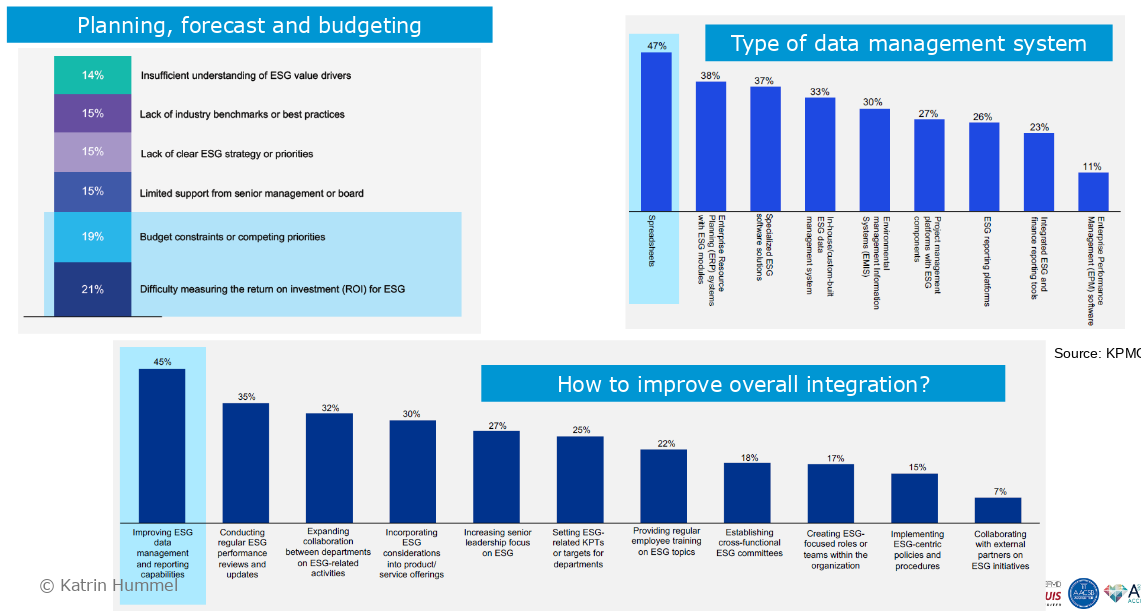
You can’t manage what you aren’t measuring
- data aspect is very bad in most companies
- most use spreadsheets
- mostly about missing standardization efforts
- not included in forecasting and budgeting either
- missing out on Strategic Foresight and Scenario Planning improvements
- if data was measured efficiently one could imagine a “race to the top” to optimize for emissions, etc
- fueled by right Incentive Schemes for C-suite and competition
Data Pyramid
- first … most important but fewest data points, last … inverse
- KPIs
- Revenue, CAPEX, OPEX → EU Taxonomy Regulation
- Datapoints require external assurance
- Datapoints require external reporting
- Potential sustainability-related datapoints
Empirical Evidence
- wontfix sr 6 34